Table of Content
- BLE Beacons
- BLE Beacons Applications
- Bluetooth Direction Finding Features
- Location Services for IoT
- Use Cases for BLE in IoT Real-Time Locating Systems (RTLS)
- BLE Mesh
- BLE in IoT Opportunities
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a globally adopted short-range communication protocol. BLE has many benefits for IoT, including lower power consumption, longer battery life, dependable performance, lower price, and ease of accessibility.
As such, BLE is an optimum choice for operations that do not require the transfer of large amounts of data.
Developing products with BLE for IoT is a key driver in innovation and solving business operations challenges. Asset-tracking solutions help businesses become more efficient in logistics, inventories, and other real-time location service needs—all of which help to optimize processes and improve operational performance with actionable IoT data.
BLE for IoT is best for creating highly efficient location services with asset tracking, item-finding solutions, access control with keyless entry, and equipment- and person-tracking.
A BLE-based asset tracking system provides advanced monitoring of sensor-based information and real-time access to and visibility of asset locations.
A lightweight sensor that transmits information via Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connection protocol through a BLE beacon in a network is embedded in an asset. Data from the asset is then transmitted to a web or mobile application to monitor and analyze assets in the network.
Also, IoT assets can be equipped with sensors that have the ability to operate outside of BLE networks, collecting information through integrated cellphones (SIM cards) using cellular (LTE, 3G, and 5G) communications, Wi-Fi hotspots, and GPS and location-based services (LBS) provided by cellphone companies.
BLE Beacons
BLE beacons are low-power Bluetooth transmitter devices with unique identifier information used to determine an asset’s location (asset tracking IoT and indoor location services) within an area. Beacons are Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) applications that come in many forms and can be installed in a fixed or mobile location, depending on the use case. BLE beacons have a component that allows devices to discover each other and determine device location.
A mobile user app recognizes the BLE beacon that broadcasts coded information (signals) and maps data to a location for triggers and actions. Information is decoded using specific frame formats, native Bluetooth APIs, or dedicated APIs from the device manufacturer.
Beacons broadcast signals within a range, and receiving devices compute the proximity using Received Power Strength Indicator (RSSI) measurements methodology (signal strength).
Bluetooth modules and chips are used as beacons. Other devices, such as a Raspberry Pi, can also be turned into beacons for Bluetooth development purposes. A BLE module is a circuit with a chipset integrated with a radio frequency module, controller, API processor, and other components for specific applications.
BLE Beacons Applications
Beacons applications are deployed for particular purposes, and there are various approaches to express locations depending on the use case. Mapping the beacon code to a location requires looking up a database in the mobile app, local server, or remote server. The distance estimation can be expressed by proximity or distance from BLE beacon points by the radio signal strength indications and a path calculation. Also, distance is calculated by radio mapping its location (fingerprinting technique) from previously registered locations. Localization with Bluetooth radiofrequency technologies can achieve distance estimates of 2 to 10 meters because of signal fluctuations and obstructions (multipath, reflections, and shadowing).
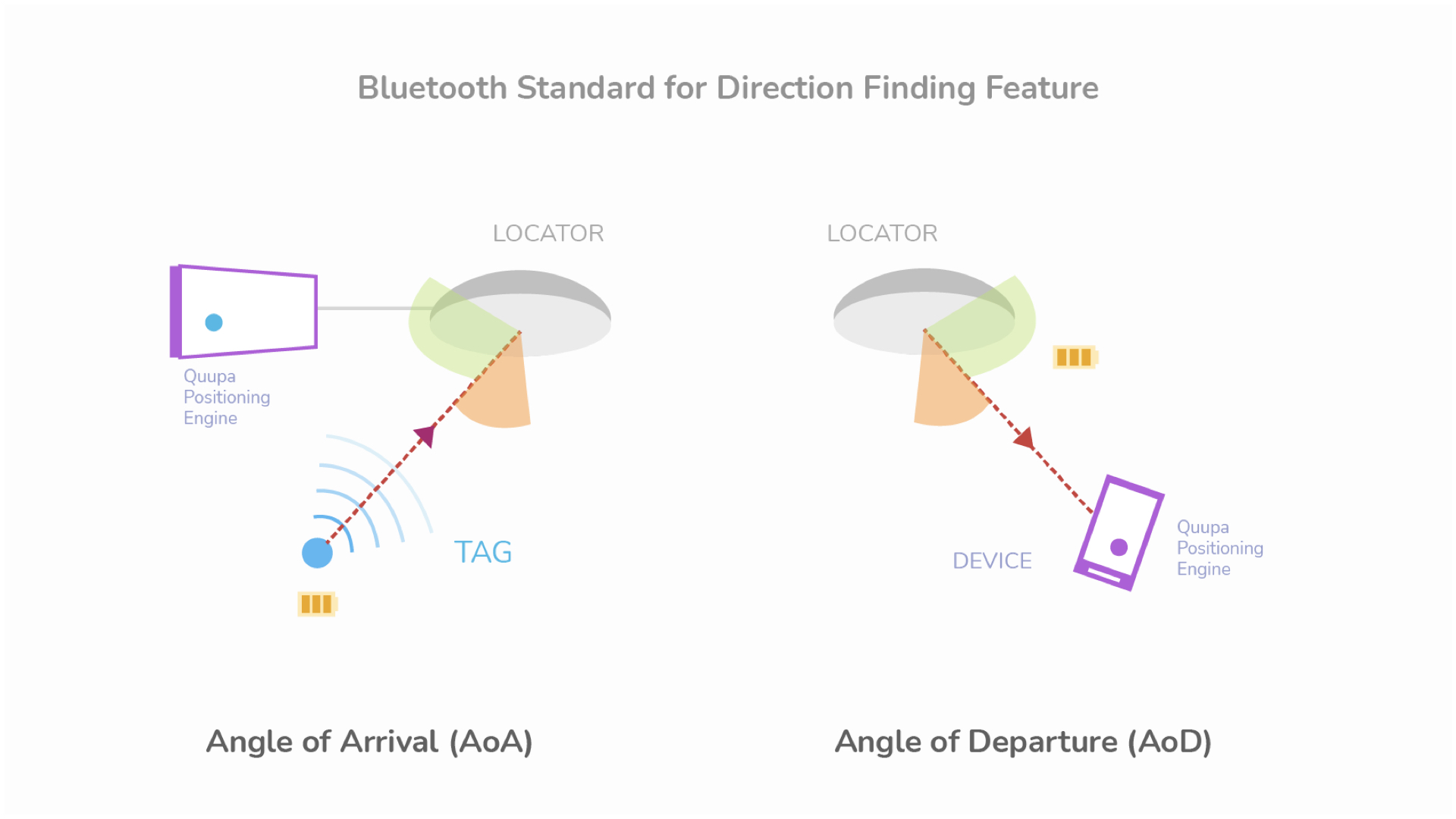
Bluetooth Direction Finding Features
Bluetooth location technologies have evolved to Bluetooth Direction Finding solutions for superior tracking accuracy. BLE finding solutions use a fixed infrastructure of locators that receive Bluetooth signals from devices (tags) while they move around. Depending on the IoT use case, direction-finding can be set up with locators and can process position calculations measuring the angular direction of radio signals, computing locations in two ways:
- Infrastructure-centric (Angle of Arrival, AoA)
- Mobile-centric (Angle of Departure, AoD)
Choosing the right Bluetooth technology for your needs depends on the direction-finding use case and its required accuracy. You can also leverage AoA and AoD methods, depending on the context of the application.
Bluetooth direction methods are optimal for rugged environments such as warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and industrial plants as they can provide greater accuracy, i.e., less than 10cm and low latency (150 milliseconds).
Tags have lower prices, however, and can have batteries that last for many years; locators are also independent. In addition, identifying location through tags is typically more accurate, as tags communicate continuously, making them very responsive with very low latency.
Beaconing solutions are simpler to set up but may require more maintenance than direction-finding solutions.
Thanks to device compatibility and interoperability benefits, BLE for IoT provides scalability and versatility to perform. For example, beacons are best for proximity use cases, while direction-finding methods are more accurate and work well for presence, proximity, and positioning cases.
Location Services for IoT
Proximity Solutions
Proximity solutions refer to the location and distance between two devices.

Item finding
Works with tags attached to personal items for tracking and locating.

Point-of-Interest Solutions
Displays information on the user’s mobile app while approaching a location.
Positioning Systems
Positioning systems are used for discovering the physical location of devices:
- Real-Time Locating Systems (RTLS): Network-centric systems used for tracking people and assets inside facilities where the information goes through a server and is reported to the user.
- Indoor Positioning Systems (IPS): Mobile-centric systems designed to track location by devices and report the user position through a mobile application. Indoor positioning systems are usually built using the Bluetooth AoD method.
- Indoor Navigation (Wayfinding): Indoor navigation uses methods to determine the user’s location and shows it on a map in the mobile application for navigation purposes.
Use Cases for BLE in IoT Real-Time
Locating Systems (RTLS)
- Indoor Navigation
- Proximity Services
- Asset Tracking and Inventory Control
- Vehicle Tracking and Control
- Equipment and Tool Tracking
- Access Control
- Person Tracking
BLE MESH
Bluetooth mesh is a many-to-many topology where devices communicate using a relay message mechanism between devices extending coverage beyond the individual nodes with high performance and reliability. BLE mesh is suitable for beaconing and asset tracking applications, building automation, smart warehousing, and lighting.
BLE for IoT Opportunities
The market opportunities for BLE in IoT location services products are endless. Popular uses include offering point-of-interest (enhancing user experiences in public places such as retail stores or stadiums), finding solutions to track items, navigating facilities, managing resources, and optimizing warehouses and facilities. Location-based services have become one of the fastest-growing areas for Bluetooth and IoT applications.