Table of Content
- Benefits of Touchless Technologies
- Types of Touchless Technology
- The Future of Touchless Technologies
Developing touchless interfaces has become critically important and necessary as consumers increasingly demand applications that reduce the need for face-to-face interaction.
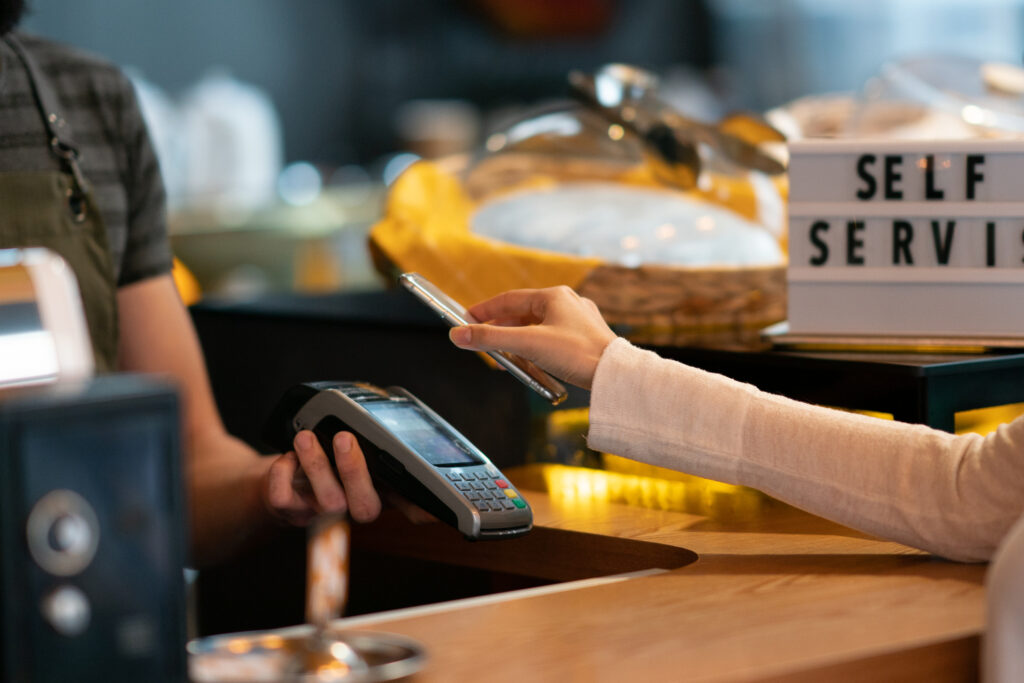
Mobile apps have been vital in the quest to replace public touchscreens with touchless experiences using technologies such as Bluetooth Low Energy, NFC, biometrics, and QR codes.
Adopting touchless technologies and transforming current solutions into rich, seamless user experiences (UX) is an accelerated trend in the marketplace. Businesses that fail to keep up with market demands are at risk of losing their competitive edge.
Touchless technologies are transforming user journeys and workflows due to behavior changes that may become permanent. A “new normal” way of interacting continues to evolve—and now is the time to catch this wave.
Benefits of Touchless Technologies
- Reduces touchpoints
- Promotes download and usage of mobile apps
- Reduces the risk of disease from touching public touchscreens
- Increases revenues
- Improves customer service
- Results in better customer insights with analytics
- Reduces wait time in lobbies
Types of Touchless Technology
Even during harsh economic times, touchless technologies bring opportunities to develop or enhance new products, giving an edge to businesses that adopt or integrate these technologies into their digital transformation initiatives.
Touchless technologies can be combined and implemented in different environments and applications depending on individual business objectives and strategies. Each technology has its strengths, and certain technologies can complement each other. Solutions are designed considering the ROI and user experience (UX) across touchpoints.
Touchless technology options include:
NFC Signage Technology. Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range communication technology. An NFC tag is a microchip containing stored information that can be read by mobile devices and used to transfer data. Customers hold their phones to signs with an NFC tag, connecting automatically with enabled devices or a contactless reader within a four-inch range, prompting use of a mobile app for performing an action, such as producing a payment confirmation or a virtual boarding pass. Examples include:
- Touchless pay apps (mobile wallets)
- Access control
- Attendance tracking
- Public transportation
- Authentication apps
Bluetooth. This technology operates when a Bluetooth Low Energy signal with an encrypted identifier is picked up by a reader, connecting a mobile app with an existing sensor and system.
Touchless check-in (touchless sign-in app) is one example of Bluetooth technology in action. Access control systems replace old access cards by registering guests through a mobile app, eliminating an in-person or iPad sign-in process, making this system particularly suitable for offices, hotel rooms, and dorms, for example. The system operates using sensors embedded in hardware connected to access control systems and mobile apps through SDKs and APIs. While users are inside a commercial building, mobile apps can run in the background, set for opening automated doors at entrances, elevators, parking areas, etc.
QR Codes/Barcodes Scan. On-demand mobile QR (Quick Response) codes provide instant access to information. A QR code is a version of barcode, an open-source technology that is easy for mobile apps to scan. QR codes can direct users to download a mobile app or visit a website. Examples of QR code use include:
- Contactless deliveries. (Couriers and food delivery services are implementing contactless delivery options that verify the customer’s digital ID, obtain instant proof of delivery and payment, and reduce losses from chargebacks as well as failed deliveries and returns. An in-app function scans or enters a code that comes in through an SMS, email, or notification from the app.)
- Intelligent lockers
- Employee IDs
- Event badges
- Touchless menu apps
- Touchless feedback forms
Touchless Biometric Authentication. Biometrics measure the physical characteristics of a person to verify the person’s identity. The use of biometrics for facial recognition is the most common as it provides the best performance in many environments. Biometrics users enroll through encrypted software. Ideal uses include:
- Retail stores. Palm recognition biometric solutions scan the hand image to provide contactless entry and payment technology, such as the recently launched Amazon One at Amazon Go stores.
- Venues and trade shows. Facial biometrics matching at walking speed provides streamlined entry to stadiums, arenas, and other venues. Also, palm recognition is a promising technology for entering a venue.
- Contactless travel. The implementation and use of biometrics to track air passengers is currently under high pressure due to passengers’ resistance to flying. Facial recognition systems must verify passengers through government databases during check-in, bag drop, TSA security, and boarding.
RFID Technology. Shoppers can enjoy a contactless experience in stores offering products equipped with RFID (radio-frequency identification) tags. These tags are automatically disabled when customers use the self-checkout option in the mobile app (Scan & Go), thereby eliminating contact between employees and customers. Benefits of RFID technology include frictionless shopping for the customer and simplified inventory management for the employees.
Voice Assistance. With this technology, users can navigate through facilities by providing voice commands that transform displays into interactive sources of information. Voice assistance can be successful in environments such as:
- Kiosks
- Touchless elevator apps
- Museums
- University and college campuses
Gesture Control. Gesture control technologies use algorithms and motion sensors to recognize and interpret movements that interact with and control a software system. For example, hand gesture recognition and mid-air haptic interfaces are developing to operate screens without touching their surfaces. This technology is well-suited for environments such as:
- Automotive
- Consumer electronics
- Home automation
- Sign language translation
The Future of Touchless Technologies
Research points to new opportunities to develop disruptive products using contactless technologies, biometrics, mobile apps, self-service, and automation that are attracting innovators and investors alike.
Investing in contactless products has become part of the digital transformation strategy of many businesses. These transformations are playing a crucial role in the post-recovery economy.