Table of Content
The Krasamo IoT Concepts Series has been created to provide clients with informational resources to increase awareness of IoT technologies and to offer considerations for helping in the adoption of IoT solutions.
IoT services and related products have seen explosive growth in the last few years for new use cases in smart homes, process automation, and operating performance, leading to high demand for IoT services.
IoT edge computing is a key technology worth considering when building IoT systems. It reinforces the deployment of workloads on IoT devices and facilitates data storage and processing in the cloud.
What is IoT Edge?
Data is transferred and received across networks and needs to be analyzed locally in real-time to respond to user needs and product requirements.
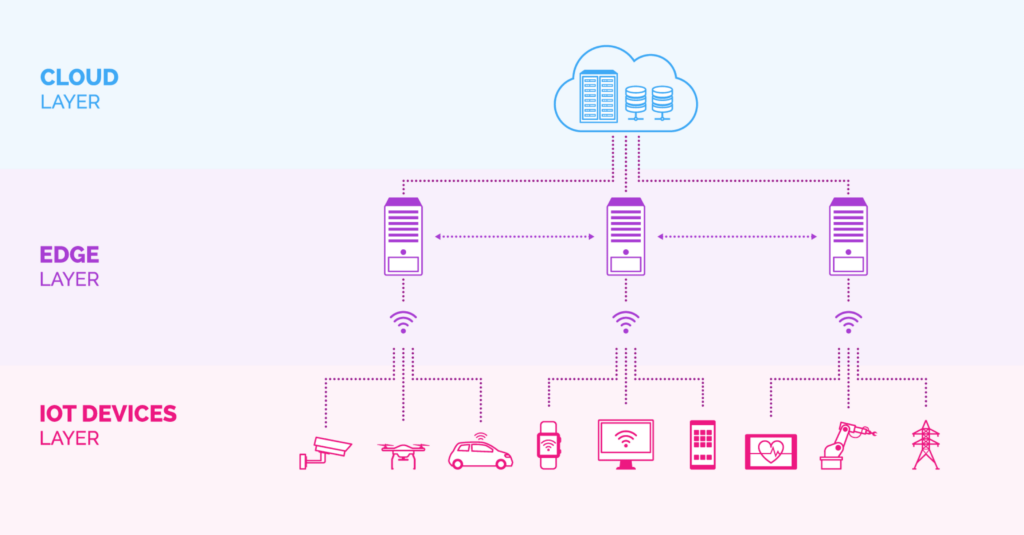
IoT edge computing is the processing and analysis of data from IoT devices near the physical location (end-points) where data is used or collected.
IoT connects physical objects to the internet. Edge computing makes operations more efficient by reducing latency and increasing network bandwidth, allowing for faster data transmission in local or offline operations, creating optimal scenarios for implementing IoT data analytics and machine learning models.

IoT Edge Devices
IoT edge computing supports IT infrastructure by providing resources to edge devices in multiple locations to support connectivity and generated data.
IoT edge devices are physically located at the network edge, such as sensors, actuators, routers, bridges, and IoT gateways, with enough storage and computing power to collect and process data.
In addition, IoT devices can also perform as edge devices and gateway devices.

IoT Edge Analytics
IoT edge computing allows us to ingest data through devices and apps that handle functionality and create a fast response, filtering and processing data on the device (at the edge) and sending it to a centralized location for storing, further processing, and transforming (ETL process).
Data is aggregated to the pipeline for a logic process and for the purpose of understanding its relationships and insights for smart analytics and business intelligence.
Then it can send the data back to the edge for the inference stage to employ its purpose and capabilities.

IoT Edge Cloud
Edge computing is part of the computing, networking, and storage infrastructure of IoT systems. It allows extending cloud services and environments to other locations to deploy workloads and run services such as containerized applications, Kubernetes, and virtual machines on IoT devices and to process its data at the edge for real-time decisions.
You can have hundreds of assets, device fleets, equipment, vehicles, and other devices connected to a central platform, computing and analyzing near the user or where the data is generated, thereby lowering response time securely and efficiently.

IoT Edge Architecture
Keeping computing power in remote locations operating independently from the central systems reduces data transmission and bandwidth costs. Enterprises must design their IoT edge architectures to handle and connect data in various stages to support real-time edge computing applications.
IoT edge computing infrastructure must have interoperable and vendor-neutral components and license-free software with the flexibility to handle hybrid workloads and use the same tools as their IT infrastructure.
IoT edge deployment options can vary by use case, and work executing code or running services locally in IoT edge devices through IoT modules or containers that communicate and send data to the IoT edge runtime. The IoT edge hub (PaaS) handles device communication, management, and monitoring of the status of operations.
You can develop, manage, and deploy IoT device software with edge runtime AWS IoT Greengrass (open source), which offers custom and pre-built components and edge-to-cloud services. Another popular solution is Azure IoT Edge for deploying the cloud on IoT edge devices.
Krasamo’s Edge Computing Services
- Develop IoT edge device apps and back-end apps
- IoT edge device provisioning
- Build custom gateways and protocols, set up MQTT and AMQP messaging protocols for IoT edge
- Configure IoT edge devices to run and deploy IoT edge modules for specific edge use cases and devices
- Create workflows of task and automation for IoT edge device management
- Virtualize products in real-time, building a digital twin system










I’ve worked with some IoT projects in my previous role, and I think it’s worth noting that while AWS Greengrass and Azure IoT Edge are both great solutions for deploying cloud services on the edge, they’re not the only options out there. Depending on the specific use case and requirements, other platforms like SAP Leonardo or Google Cloud IoT Core might be more suitable. As an IT pro who’s dabbled in IoT consulting, I can attest that evaluating these different options carefully is crucial when implementing IoT edge computing solutions. Thanks for sharing this informative post!
I appreciate the effort to elucidate the concept of IoT edge computing, but I must emphasize that this narrative oversimplifies the intricacies involved. For instance, IoT edge devices often employ a layered architecture, with various components interacting through standardized protocols such as CoAP or MQTT. Furthermore, many applications require more sophisticated processing capabilities than mere data filtering and aggregation. It’s also worth noting that the distinction between IoT edge analytics and cloud-based services is not always clear-cut.
I must say, this post does a decent job of explaining IoT edge computing concepts, but I’ve seen more comprehensive coverage from industry experts who offer internet of things consulting services. Still worth a read.
Meh, just another generic edge computing services list. Would be more impressive if you discussed real-world use cases and highlighted how partnering with top iot consulting companies can streamline development and reduce costs.
I completely agree with your assessment of IoT edge devices! In my experience, having a robust IoT edge computing infrastructure is crucial for enabling real-time insights and decision-making in various industries. As an advocate for IoT consulting, I’d like to add that edge analytics can also be applied to predictive maintenance and anomaly detection use cases, which can significantly reduce operational costs and improve overall efficiency.
Great summary on the importance of IoT edge computing! 👏 As a business analyst with experience working with IoT consulting companies, I can attest to its game-changing potential. By processing data locally, it enables real-time analysis and faster decision-making, making it an essential component for optimizing IoT systems. Thanks for shedding more light on this fascinating topic!
I’m loving the rundown on Krasamo’s Edge Computing Services! It’s great to see companies exploring IoT edge computing, which is totally changing the game for real-time data processing. I’d also like to mention that internet of things consulting can be really helpful in identifying and implementing use cases for IoT edge devices. Keep it up!