Table of Content
With the emergence of IoT technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and home automation, the smart lock category is positioned for significant growth in the coming years. Recent product developments, successful implementations, strategic partnerships, and innovative new features signal that smart locks are gaining worldwide adoption.
At Krasamo, we see business opportunities across multiple application segments—residential, hospitality, enterprise, and infrastructure—as well as across various smart lock types, including deadbolts, padlocks, lever handle locks, server locks and latches, knob locks, and others.
Building on the foundational concepts covered in our previous blog post on smart lock design basics, we are ready to explore emerging trends and underlying technologies shaping the future of smart locks. We aim to set the stage for further engagement with our IoT development team.
Evolving Landscape
Early smart lock designs focused on secure electronic access control, low-power operation, and seamless connectivity using protocols like Zigbee, Bluetooth LE, and Thread. These foundational principles enabled the replacement of traditional keys with digital credentials and the integration of smart locks into broader home ecosystems.
While 2024 was a good year for smart locks—with manufacturers fine-tuning software and hardware integrations and addressing challenges in interoperability—the smart lock category emerged as a strong performer. Innovations like facial recognition, biometric methods, and Matter-enabled devices showcased the potential for more intuitive and secure access control.
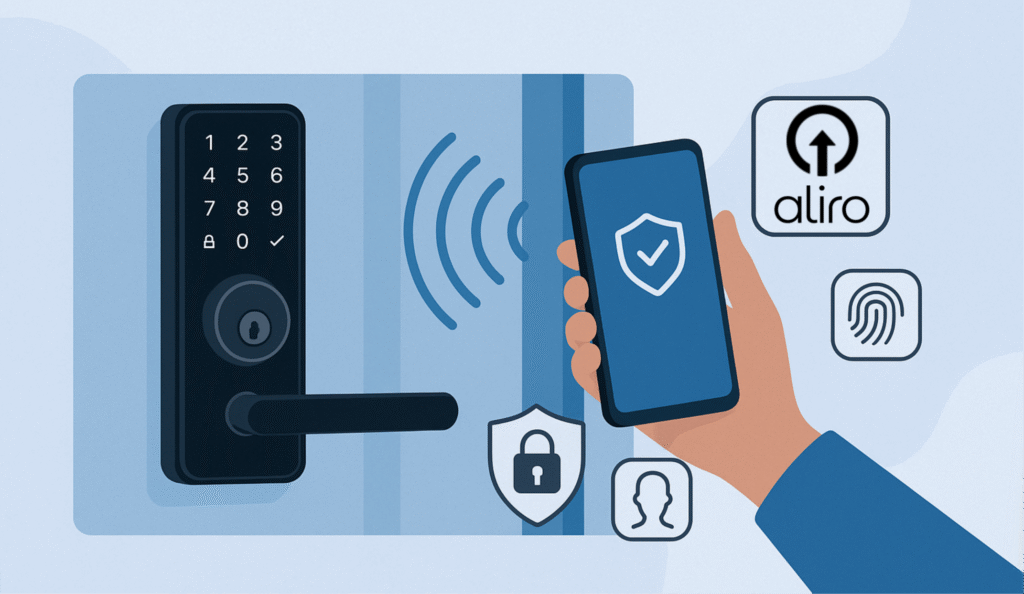
Looking ahead, we expect 2025 to be a breakthrough year for smart locks. Next-generation devices will navigate complex multi-protocol environments, incorporate advanced authentication methods, and introduce cutting-edge features such as ultra-wideband (UWB) hands-free unlocking and the upcoming Aliro protocol. These advancements promise robust performance, enhanced security, and frictionless user experiences—all while optimizing power efficiency and managing production costs.
Challenges and Strategic Considerations in Smart Locks Design
Ecosystem and Protocol Complexity
As smart lock products evolve, ensuring interoperability within the IoT ecosystem remains a significant challenge. Devices must support a variety of wireless protocols—such as Zigbee, Bluetooth LE, Thread, Matter, and even Wi‑Fi—to maintain reliable connectivity in low-power or network-constrained environments f!.
In addition, these devices must operate autonomously while integrating smoothly with broader smart home ecosystems like HomeKit, Google Assistant, and Alexa. Overcoming both hardware-level and software-level integration challenges—such as implementing dual/multi-authentication schemes and real-time OTA firmware updates—is essential.
Moreover, interoperability and frictionless user experiences will be enhanced by emerging protocols. The upcoming Aliro protocol (discussed later) promises to standardize secure credential exchanges between user devices and access control systems, further simplifying the ecosystem complexity faced by smart lock designers.
By initially leveraging NFC for tap-to-unlock—and optionally incorporating UWB for precise, hands-free unlocking—Aliro offers flexibility without being solely dependent on any single technology.
Selecting a platform that supports large-scale, secure networks with pre-certified stacks and robust reference designs is crucial. This ensures that even battery-operated devices maintain high performance and reliability.
Enhanced Authentication and Access Control
Several authentication methods—from traditional PINs to advanced biometrics like fingerprint and facial recognition—are fundamental to smart lock design. Recent innovations have even introduced methods such as proximity-based auto-unlocking and voice recognition that respond to your presence, streamlining access while maintaining rigorous security.
However, while advanced biometrics offer rapid access, they can sometimes be fuzzy, and incorporating multiple modes inherently increases system complexity.
Balancing robust security with a seamless user experience is a top priority. Emerging protocols like Aliro promise to standardize secure, cross-platform digital credential exchanges, ensuring that authentication remains convenient and reliable. At the same time, implementing end-to-end encryption, secure boot processes, and tamper-resistant hardware is needed to protect against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Ultimately, next-generation smart locks will integrate diverse authentication methods to deliver multi-layered security without compromising ease of use, transforming the way we interact with our front doors.
Optimizing Power and Performance
Smart locks are typically battery-powered, making energy management a critical design challenge. Selecting the right microcontroller unit (MCU) is important for delivering the necessary wireless performance while extending battery life. Ultra-low-power, single-chip wireless microcontrollers can run algorithms and transmit data using sophisticated power management techniques—such as efficient sleep modes and optimized active currents—to support multi-year battery life, a prerequisite for today’s wireless locks and energy harvesting applications.
Additionally, system-on-chip (SoC) solutions specifically designed for energy harvesting—with unique ambient IoT capabilities—further enhance power efficiency. A robust over-the-air (OTA) update mechanism complements these hardware features by enabling continuous feature improvements and ensuring secure operation without frequent battery replacements or manual updates.
Manufacturing, Cost, and Scalability
Cost-efficient development and production are key to market success. Krasamo’s IoT engineers balance low-cost components with high performance to ensure affordable production without sacrificing reliability.
Leveraging pre-certified modules, reference designs, and well-documented SDKs reduces development time and associated risks. Pre-certified modules, which are rigorously tested to meet industry standards, integrate with other components—reducing debugging time and enhancing overall reliability, thereby lowering the chance of hardware failures.
Aliro Smart Lock
What is Aliro? Aliro is an industry-standard access credential and communication protocol specifically designed for smart locks. Developed through the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA) by major industry leaders—including Apple, Google, Samsung, Silicon Labs, and prominent lock manufacturers—Aliro aims to deliver a secure, consistent, and unlocking experience across a range of devices such as smartphones, smartwatches, and other wearables.
In its initial phase, Aliro focuses on enabling interoperability between end-user devices and access control systems, ensuring that devices can securely and reliably replace traditional keys.
By leveraging technologies such as NFC for tap-to-unlock and ultra-wideband (UWB) for precise, hands-free unlocking, Aliro extends beyond existing solutions like Apple’s Home Key.
UWB, in particular, enables a lock to determine a user’s exact position and approach direction, allowing the door to unlock automatically as the user nears—without any physical interaction.
While Aliro initially supports NFC as the primary means of secure key exchange, it can also leverage UWB to deliver a more precise, hands-free unlocking experience without being solely dependent on it— (Aliro is meant to support both NFC and BLE + UWB, but only NFC will be mandatory and support for BLE + UWB will be optional for each manufacturer).
The Aliro protocol is still under development, with a targeted release in 2025. Once launched, it is expected to simplify integration across various platforms and verticals—from residential and corporate environments to hospitality and beyond—ensuring the mobile access experience remains secure and frictionless.
Furthermore, Aliro complements other standards, such as Matter, which focuses on overall smart home interoperability, by standardizing secure communication between digital devices and locks.
Overall, Aliro represents a significant step forward in smart lock technology, promising to transform access control and enhance smart home ecosystems’ convenience, security, and interoperability.
Ultra-Wideband (UWB) in Smart Lock Design
Ultra-wideband (UWB) is an emerging radio technology that offers highly precise ranging and localization capabilities, making it a game changer for smart lock design. Unlike traditional wireless technologies that rely on signal strength or complex triangulation methods, UWB sends short, high-frequency pulses across a wide spectrum, enabling a smart lock to accurately determine the distance, position, and even the angle of a paired device—such as a smartphone or smartwatch—down to a few centimeters.
UWB enables a truly frictionless, hands-free unlocking experience. As a user approaches their door, a UWB-enabled smart lock can detect the exact proximity and direction of the device, automatically initiating the unlocking process without any physical interaction. This precision significantly reduces latency and uncertainty compared to auto-unlock methods based solely on Bluetooth or NFC. Moreover, UWB’s ability to precisely assess a user’s approach enhances convenience and helps prevent unauthorized access by mitigating the risk of relay attacks.
By integrating UWB with protocols like Aliro—which standardizes secure access credential exchanges—smart locks can combine the ease of automatic, hands-free access with the robust security required in modern smart home ecosystems.
Industry Innovations and Accelerated Time-to-Market
Recent collaborations in the industry are accelerating the development of next-generation smart locks. For instance, Nordic Semiconductor and Qorvo have launched a reference application for access control systems that leverages the upcoming Aliro protocol and Matter. Based on Nordic’s nRF54L Series ultra-low power multiprotocol SoC and Qorvo’s QM35825 UWB SoC, this reference design demonstrates how combining micro-location accuracy with secure, low-power wireless connectivity can streamline smart lock design.
This solution lets developers quickly integrate wireless protocols, including NFC, Bluetooth LE, and UWB. As a result, smart lock development becomes more accessible for manufacturers, and time-to-market is significantly reduced.
Krasamo’s Experience in Smart Lock
At Krasamo, we develop end-to-end smart lock solutions that effectively combine secure hardware design and robust software integration. In one project, we built a remote smart lock management system that integrates with mobile devices and voice assistants, overcoming challenges such as firmware synchronization, secure cloud communication, and voice command responsiveness.
On the hardware side, we optimized power consumption by replacing an always-active polling mechanism with hardware interrupts and implemented over-the-air (OTA) updates to keep devices secure and up-to-date.
Our approach ensures that smart locks are secure, low-power but also user-friendly, and scalable for diverse market segments.
Krasamo’s comprehensive IoT expertise transforms smart lock development, enabling faster time-to-market and reliable, next-generation access control solutions.
Krasamo’s IoT Development and Consulting Services
Given the challenges and opportunities in developing advanced smart locks, partnering with a company with proven expertise is essential. Krasamo offers end-to-end IoT development services that span PCB layout, embedded firmware development, wireless integration, and compliance with evolving smart home standards (including Matter). Our deep technical knowledge ensures that every aspect—from chip selection to final product deployment—is executed with precision, helping you navigate the complexities of implementing next-generation smart lock features and accelerate your time-to-market.











I agree that partnering with an experienced firm like Krasamo’s IoT development and consulting services would be beneficial for companies looking to implement advanced smart lock features. Internet of things consulting expertise is indeed crucial in this space.
I’m not blown away by this tech, but I can see how UWB would be a solid addition to IoT consulting services for seamless smart lock experiences. Still, feels like NFC has been doing similar things for ages.
🤖 I completely agree that IoT tech is revolutionizing the smart lock industry. One thing that caught my attention was the mention of UWB (Ultra-Wideband) tech, which enables hands-free unlocking. Interestingly, UWB also uses the Aliro protocol for efficient data transmission. It’s fascinating to see how these emerging trends are converging to create seamless experiences! 💻
Great post! I’m loving the direction this industry is headed. With the emergence of Matter and Aliro protocol, it’s exciting to see the accelerated innovation in smart locks. The reference application from Nordic Semiconductor and Qorvo showcases how combining UWB with secure wireless connectivity can enhance smart lock features, like hands-free unlocking, making it a game-changer for access control systems. Looking forward to seeing more collaborations like this!