Table of Content
A mobile app’s journey begins with an idea, often conceived to provide value to customers and potentially generate revenue. App ideas frequently develop as extensions of existing products or emerge when businesses seek new or underutilized productivity tools.
Essential to this initial stage is thorough market research, which assesses the idea’s potential and aligns it with business and marketing objectives. For stakeholders, crucial factors that determine the feasibility of the app idea include product potential, market size, market needs, and consumer attitudes, among other relevant information.
Understanding the market is just the first step. The real challenge lies in translating these insights into a product that resonates with users. This is where collaboration between the marketing and UX (User Experience) teams becomes indispensable. While the marketing team brings in-depth knowledge of the market dynamics and consumer preferences, the UX team contributes insights into user behavior, needs, and design best practices. This collaboration is vital in shaping the app idea into a product that meets market demands and provides an exceptional user experience. The integration of these teams ensures that the app design is market-driven and user-centered, combining the best of both worlds to create a product that stands out in the competitive app landscape.
The path to a successful app requires more than an idea; it demands a strategic approach. This involves brainstorming solutions, validating the concept’s relevance, and ensuring it fulfills a genuine need. Preparing a detailed business plan or developing a prototype is key, particularly for those seeking investment, as it showcases the idea’s practicality and your commitment.
In the following sections, we will delve into the critical roles of UX teams in the app development process. We’ll explore their contribution to refining app ideas, the significance of UX research, and transforming initial concepts into MVPs. These MVPs are vital for assessing market interest and evolving the idea into a practical and appealing application.
UX Teams
The UX (User Experience) team plays a crucial role within the overall team structure, significantly influencing the UX design thinking process. UX design, an art that evolves based on the team’s skill sets, available resources, and the complexity of projects, is integral to mobile app development. A key aspect is the synergy between the developers and the UX team; any gap in expertise can be a critical factor in the agile development process.
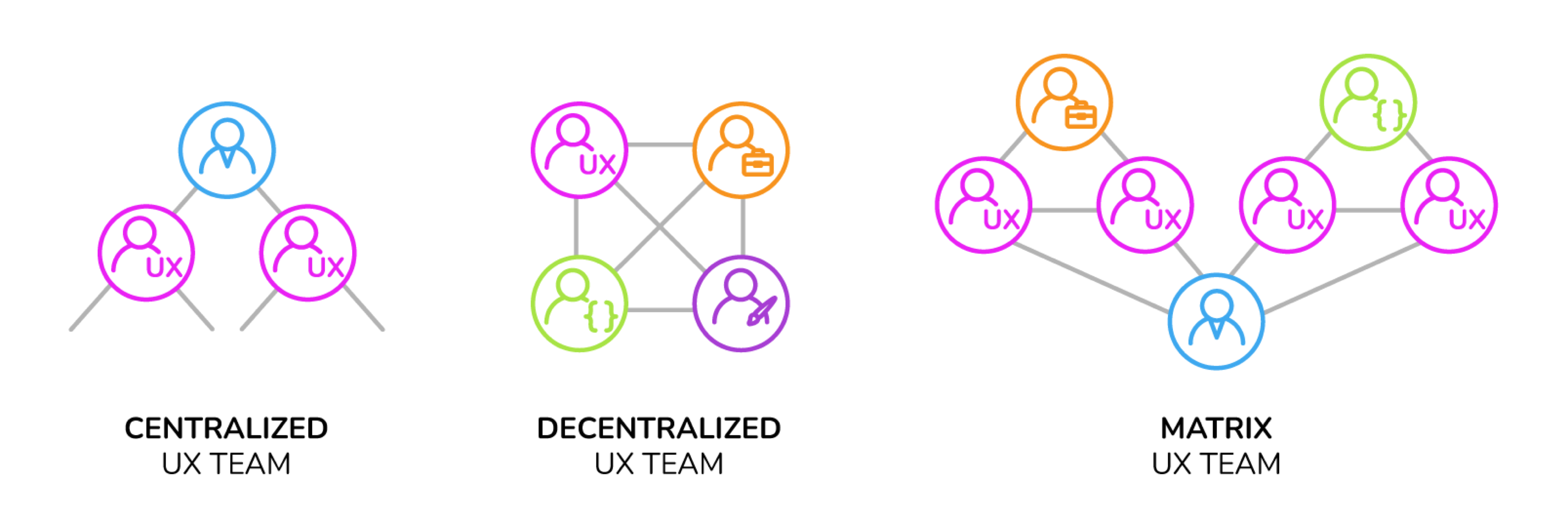
In digital product development, a UX team member often leads product design. The integration of UX teams within an organization can vary. They might report to marketing departments (under product managers), belong to a centralized UX team, or be part of a hybrid structure. A typical UX team includes UX researchers, designers, analysts, product managers, and team leaders, among other roles.
Centralized UX Teams. A centralized UX team operates across various projects as required, reporting to a UX manager. This model positions team members as consultants for UX efforts within the organization, allowing them to contribute to multiple teams. Commonly employed by specialized UX agencies, this structure features multiple levels of UX management. Centralized teams are known for their enhanced UX skill sets, resources, and comprehensive knowledge base.
Decentralized UX Teams: UX team members are dedicated to specific products or features in a decentralized setup. They report directly to product teams, becoming knowledgeable about their assigned product lines. This close involvement in product planning offers them greater opportunities for contribution. However, the absence of unified UX management can sometimes lead to reduced productivity.
Matrix UX Teams: Matrix UX teams report to the product team lead and the UX manager, necessitating a well-integrated and flexible approach. This structure is essential for developing a long-term strategy that effectively aligns the product and UX teams. The dual reporting lines require clear communication and coordination to ensure the success of UX initiatives.
UX Research
User Researchers (URs) play a crucial role in UX teams by helping them learn about and understand their users. They ensure that app features align with customer needs. URs are instrumental in challenging assumptions about users and mitigating biases, which is vital for avoiding UX issues. Integrating UX research with design early in the project is essential to the success of the iterative design process, as it exposes the design team continuously to research and user observations.
UX researchers collaborate with business analysts, prototype developers, and designers, contributing significantly to the design thinking process and fostering innovative solutions. They employ a variety of research approaches in a repeating, non-linear process to address different research questions, ensuring the team is always equipped with fresh data.
The key tasks of UX researchers include interviewing users and observing their actual behavior to provide actionable and testable insights about user needs. Since observed behavior is often more reliable than self-reported data, understanding user actions within their real-life context is crucial. Contextual inquiry, a method and framework for observations, guides how research is conducted and how user stories are collected.
Emphasizing a User-Centric Approach in App Development
A user-centric approach should be the guiding principle in every app development phase, from ideation to final testing. This means prioritizing the end-users’ needs, preferences, and behaviors above all else.
By adopting a user-centric approach, developers and designers can ensure that the app solves a problem and does so in a way that is intuitive, enjoyable, and valuable to the user.
It involves continuous user feedback, empathy for user challenges, and an iterative design process that refines the app based on real user data.
In the ideation stage, this translates to validating app ideas against user needs rather than assumptions. During the design phase, it means creating interfaces and experiences that are aesthetically pleasing, user-friendly, and accessible.
In the development and testing phases, a user-centric approach requires rigorous usability testing and openness to changing the app based on user feedback.
This approach leads to higher user satisfaction and better user engagement and significantly reduces the risk of costly redesigns and reworks post-launch.
Different Types of UX Research:
- Qualitative Research: Offers deep insights into user behaviors and attitudes through observation and interpretation.
- Quantitative Research: Involves collecting data from larger populations using measurement systems and analytics tools, with data analyzed mathematically.
- Attitudinal Research: Focuses on exploring people’s beliefs and mental models, particularly how they think they will behave in specific contexts.
- Behavioral Research: Investigates what people do in given contexts.
UX Strategy
Data-driven marketers leverage both qualitative and quantitative analysis of Mobile Apps to gain insights into user activities. This approach enables them to tailor app functionality more precisely to meet user needs. The UX strategy, crucial in this process, is articulated through the UX roadmap. This roadmap prioritizes usability while aligning tasks with the broader goals and objectives of the organization.
Discovery Stage
The product discovery stage is the initial phase, where app ideas are explored by researching and gathering relevant information. This stage is crucial for understanding a problem and its context. Effective discovery ensures that the product is adapted to customer needs, aligns with the organization’s goals, produces better outcomes, and minimizes risks. However, this process can be challenged by inadequate knowledge of conducting effective discovery, delivery urgency, limited resources, or lack of management support. Notably, the discovery stage focuses on gathering observations and learning about the best resources to invest in rather than hypothesis testing.
Target Audience: The primary users of the Mobile App. While initially narrowing down the target audience through segmentation is beneficial, maintaining a broader audience as a long-term goal is advisable. Understanding users’ behaviors and motivations is vital for app development. Conducting both demographic and psychographic (attitudes, beliefs, aspirations) research is essential for crafting marketing messages that resonate with specific groups. This approach enhances the organization’s capacity to meet customer needs. A good practice is to start with current customers and gradually expand the target audience.
Discovery and Exploratory Qualitative Research Methods
Here are some methods to collect in-depth information about people’s opinions, thoughts, experiences, and feelings. The goal is to understand user needs and how to address them effectively with our product.

User Interviews
In user interviews, one person is questioned in a session to gather data, perceptions, and feedback about the Mobile App. These interviews are conducted with individuals from diverse demographic groups and in various circumstances, and they take place at multiple stages of the design process.

User Journey Mapping
A user persona is visualized as interacting with the Mobile App through various stages of use, including downloading, account creation, navigation, and more. This visualization maps out potential behaviors, actions, and emotions throughout the user journey, providing valuable insights into the context of use. Observations are then chronologically grouped into common tasks and phases that align with the application’s functionality.

Competitor Studies
Competitors and their successful products are thoroughly evaluated, often utilizing video comparisons to assess different products. The objective is to gain a deep understanding of competitors’ offerings, which then informs the design process to create an even better product.
Tree Testing
In tree testing, users are tasked with navigating through a text-based version of the app’s structure to perform specific tasks or explain how they would accomplish them. This method evaluates the app’s conceptual organization and feasibility without the influence of visual design elements, focusing solely on the logical flow and user experience.

Focus Groups
In focus groups, a moderator facilitates a group discussion where participants express their behaviors, attitudes, preferences, and experiences. This setting allows for a dynamic exchange of ideas and perspectives among diverse individuals, offering rich insights into collective and individual viewpoints.
Affinity Diagramming
In affinity diagramming, data from research observations are systematically categorized and grouped. This process involves identifying key themes and patterns within the data, which are then organized into clusters. These clusters facilitate the development of insightful interpretations, providing a deeper understanding of user needs, mental models, workflows, and other critical aspects. This method is instrumental in synthesizing complex information and uncovering connections that might not be immediately apparent.

Remote User Research Studies
Remote user research studies are conducted using digital tools to gather user insights without physical presence. This method enables global participant reach, offering flexibility and convenience for both researchers and users. It involves video conferencing and online surveys to collect user behavior and preferences data. While cost-effective and efficient, remote research can face challenges like technical issues and limited observation of non-verbal cues.
Social Media Analytics
This method utilizes data from social media platforms to understand the existing app audience. Researchers can glean insights into users’ opinions, thoughts, and preferences by analyzing interactions, comments, shares, and demographic information of users engaging with the app’s social media content. This process helps understand the audience’s needs, behaviors, and attitudes towards the app, guiding the refinement of product features and marketing strategies to address user requirements better.

Field Studies (Ethnography)
This method involves observing user behavior in their natural environment to understand their needs and workflows better. Field studies are diverse and tailored to the specific requirements of each project. The design team sets the objectives for these studies (field visits), ensuring they align with the overarching goals of understanding user interactions and environments.

Stakeholder Engagement
This method involves presenting stakeholders with detailed insights about users’ needs, challenges, and experiences with previous products. It includes discussions on user behavior, often based on well-informed assumptions and existing knowledge about the user base. The primary goal is to enhance stakeholder understanding and support (buy-in) for the project, ensuring alignment with user-centric objectives.

Diary Studies
Diary studies involve participants recording their daily interactions, thoughts, and feelings over a specific topic or product. These entries provide longitudinal insights into user behavior and experiences in real-life contexts. Valuable for capturing evolving user perspectives, diary studies are instrumental in informing product development and UX design. It’s important to note that this method complements the contextual inquiry method rather than replaces it.

Workshops
Workshops are interactive group sessions that foster active participation and collaboration among team members. The primary aim is to achieve a consensus on user needs, brainstorm solutions to problems, and engage in productive discussions about app ideas, goals, and related topics. Workshops are instrumental in harnessing collective insights and facilitating a shared understanding within the team.

Surveys
Surveys involve administering structured questions to a large group of respondents. The aim is to capture various attitudes, preferences, and experiences related to a specific topic. While often used for quantitative data, surveys can yield qualitative insights, particularly when open-ended questions are included. The goal is to gather information that is both broad in scope and rich in detail, enabling statistically significant analysis.

Empirical Methods
These methods rely on objective observation and experimentation to understand user experience and enhance usability. They involve gathering empirical evidence through direct or indirect observation and controlled experiments. UX professionals often employ a tailored mix of these approaches, depending on the project’s specific needs and goals. This methodology is crucial for validating assumptions about user behavior and interactions with products.

Expert Reviews
In this method, usability issues are uncovered and identified through the analysis of seasoned field experts. These professionals scrutinize the product to evaluate its usability, interface, and overall user experience. Their insights are based on established usability principles and their extensive experience. This process is essential for identifying potential problems that might not be immediately apparent to users or designers.
Exploration Stage
Mobile App Ideas—Ideating and Testing
Ideation involves generating ideas that have the potential to solve problems and enhance user experience. It requires a deep understanding of user needs identified in the discovery stage. The aim during ideation is to produce a broad range of app ideas without immediate judgment. Ideation groups discuss app ideas, goals, and benefits and then progress to prototyping with the most promising concepts, especially in the context of a redesign. Tools like pen and paper, sticky notes, and whiteboards are used for sketching and creating wireframes. Mockups and individual screens are also developed for testing, though typically without navigation.
Testing in the Ideation Stage
Testing at this stage provides feedback that helps refine the app idea and continuously improve the prototype for a better UX design. The data gathered from testing also offers insights to refine the problem definition further.
Concept Development
The concept development plan should be supported with marketing research before being presented to stakeholders. This stage usually comes before the design and A/B testing.
Define Stage
The define stage is centered around pinpointing the user problem and exploring solutions. The project team should seek innovative opportunities, establish a clear mission with concrete goals, and synchronize viewpoints to minimize friction during the design process.
User Needs Statement
It’s crucial to articulate what the app aims to achieve for the customer. The user needs statement should identify the user (customer persona), their needs, and the app’s purpose. Key questions include: What will the Mobile App accomplish? What is the goal of the app? What problem will it solve? Also, incorporating a method to measure the accuracy and success of this needs statement is important. This statement sets the foundation for the project team’s goals, paving the way for the ideation stage.
User Persona
A user persona is a detailed profile of an imaginary user characterized by specific needs. This profile is created after conducting contextual research, affinity diagramming, and user surveys. By identifying a small number of personas with distinct behaviors, motivations, and explicit goals, the team can better understand the user persona’s objectives, which is essential for making informed design decisions.
App Features
App features refer to the distinctive characteristics or prominent attributes within a Mobile App that benefit users. It’s common for customers to focus on developing features that may not be essential or widely used. Research shows that a significant portion of the development budget is often allocated to features that only a small fraction of users utilize.
This misalignment is typically due to a lack of research, leading to a bias toward developing irrelevant features and neglecting the ‘hook’ that truly engages users. Key features significantly impacting user experience include simplicity, responsiveness, intuitiveness, security, resolution, push notifications, feedback mechanisms, integration capabilities, and payment formats.
A well-executed UX design process is critical for identifying the specific features that will make the app successful for its target audience. The Krasamo UX team, for instance, employs analytics tools to discern which features are most useful and rewarding for the average user, ensuring that development efforts are aligned with user preferences and needs.
App Design
App design is an iterative process in which UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface) professionals work to develop a mobile application that addresses a specific user problem or need.
App Design Process
Sketching
Sketching is a technique that represents a design, predominantly used in the ideation stage. It facilitates the visualization of concepts and the comprehension of challenges and can be executed manually with paper and pen or digitally.
Storyboards
Storyboards are graphic illustrations that depict a story within a specific context. They feature user personas in a sequence of panels, each representing a step in a scenario. This method effectively presents research data and illustrates user interactions with the app.

Wireframes
Wireframes are structured layouts that represent the design of an app screen, showcasing data and UI elements. They evolved from sketches and can be created on paper or digitally. This process transforms initial concepts into low-fidelity prototypes or mockups, providing a clearer, more detailed view of the app’s design.

Low-Fidelity Prototypes
Low-fidelity (lo-fi) prototypes are essential for testing iterations and gathering feedback in the early design stages. They focus on visuals, app behavior, and user flow. As the design process advances, these lo-fi prototypes are further developed into more detailed mockups.

Low-Fidelity Mockups
Lo-fi mockups, positioned between wireframes and high-fidelity prototypes, are used to explore visual design aspects. They offer a preliminary view of the app’s final appearance on screen before the design is finalized and coding begins.

A/B Testing
A/B testing, a method for evaluating design elements in an app, compares different design choices, such as layouts, buttons, colors, and other details. This technique uses analytics tools to assess which variations perform better and influence the final design.

Interactive Prototypes
High-fidelity (hi-fi) prototypes in the context of the app design process are advanced, detailed, and interactive models that closely resemble the final product in both appearance and functionality.
Usability Testing
Usability testing involves evaluating a mobile app by having real users interact with it. The primary aim is to observe how easily and effectively users can navigate and utilize the product, identifying any issues that hinder its usability. This process is essential for understanding the user experience from the perspective of actual users rather than designers or developers.

Interactive Screens
Interactive Screens’ refer to a series of screens created specifically for testing purposes. These screens, designed without integrated navigation, allow designers and testers to focus on individual aspects of the user interface and interaction, providing valuable insights into the app’s usability and user experience.
Prototype and Test Stage
In the Prototype and Test Stage, app ideas are transformed into MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) and final products through the use of prototypes and testing. A prototype is a sample of the app’s final version, created to evaluate how users will interact with it.
Prototypes can be developed early in the design cycle and continuously refined with different levels of detail and functionality. They can be created using various methods, such as on paper, digitally, or HTML.
At Krasamo, we leverage both manual techniques and AI-powered UX tools to enhance the skills of our UX researchers, strategists, and designers. This approach facilitates faster prototyping and testing, resulting in improved user experiences.
Integrating AI into the UX design process allows for quicker feedback and answers to questions, ultimately expediting the analysis and interpretation of UX data. This, in turn, enables us to provide users with high-quality recommendations and useful app functionality more efficiently.
Handoff Process from Designer to Developer
The handoff of a mobile app design from designers to developers is a critical stage in app development. It involves transferring the design and its specifications from the design team to the development team, who will implement it.
Finalization of Design: The design needs to be finalized before the handoff. This involves ensuring all screens, elements, and interactions are designed per the requirements. The design should be responsive and adaptable to different screen sizes and resolutions.
Design Specification: Designers create a detailed design specification document. This document includes information about the layout, colors, typography, spacing, and other visual elements. It also describes interactions and transitions, like when a user clicks a button or swipes a screen.
Using Design Tools: Many modern design tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, Figma, or Zeplin are used to create and share designs. These tools have features for creating style guides and specifications directly within the project. They allow designers to annotate their designs and provide interactive, clickable prototypes.
Asset Preparation and Export: Designers must prepare and export all the necessary assets, icons, images, and fonts. These assets should be optimized for mobile platforms and provided in the correct formats and resolutions.
Design System and Style Guide: A design system or style guide is often created to maintain consistency across the app. It includes guidelines on how components should look and behave, ensuring the app remains consistent when developers add new features or screens.
Collaboration and Communication Tools: Tools like Slack, Jira, or Trello facilitate communication between designers and developers. These tools help track progress, discuss issues, and maintain a clear line of communication.
Review and Feedback Loop: Once the developers implement the design, there should be a continuous review process. Designers should be available to provide feedback and clarifications. This process helps ensure the implemented design stays true to the original vision.
Testing and Quality Assurance: After implementation, the design must be tested across different devices and operating systems to ensure it looks and works as intended. Any deviations or issues are reported back to the development team for fixes.
Documentation and Handover: Finally, comprehensive documentation of the design and development process, including any special cases or exceptions, is handed over. This is useful for future reference and any new team members joining later in the project.
This handoff process is crucial for successfully transitioning from design to development, ensuring that the final product accurately reflects the intended design and provides a seamless user experience.
Key Take Away
The UX researcher is one of the most important roles within the UX design process. Conducting UX research properly at the beginning of the process—in particular, before any company funds are committed to software development—is wise and will make a difference in the project’s success rate.
In addition, developing the UX persona is one of the most challenging aspects of the design process. It is an art, often based on intuition, depending heavily on the accumulated experience and know-how of the design team.
Krasamo has been working with UX projects and Mobile App development since 2010, gaining considerable user experience expertise and building a team of highly skilled designers and developers.
Using a systematic approach with a mix of proven techniques and methodologies has been the secret sauce in many of the recognized UX projects Krasamo has developed for current customers.












0 Comments