Table of Content
- Why Choose Agile Development?
- Principles and Values of Agile Development
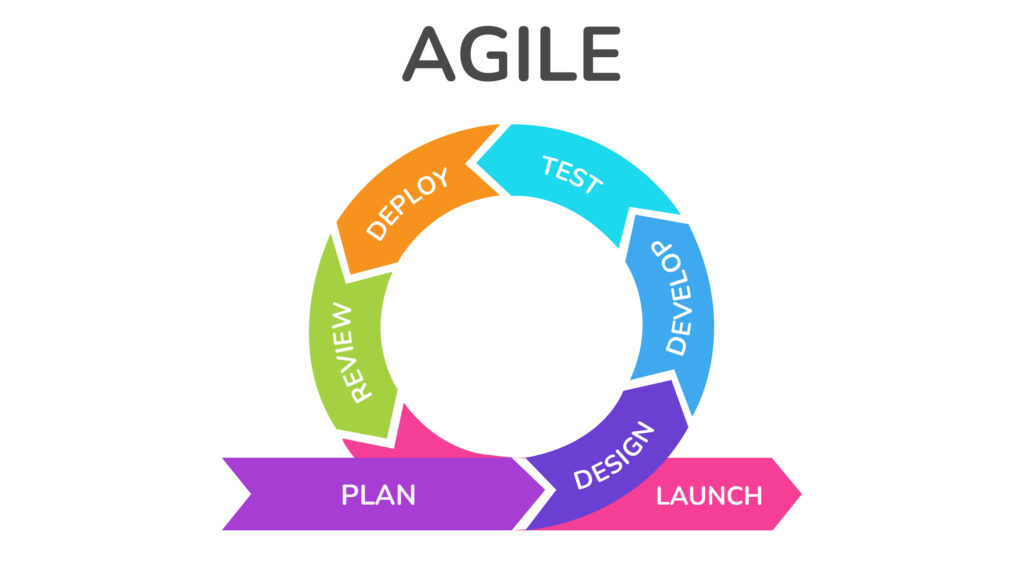
- Agile Development Process
- Key Activities Within Each Agile Sprint
- Agile Methodologies & Frameworks
- The Agile Development Process in Practice
- Scrum Artifacts & Events
- Measuring the Agile Development Process—Execution Predictability
- Tools for Agile Development
- Scaling Agile and DevOps
Agile Development began during the software-industry boom in the 1990s, accelerating the pace of innovation and competitiveness, prompting companies to adapt by adopting more flexible processes and approaches.
Market forces pushed for more innovative applications that require lightweight, agile development processes, as opposed to waterfall methods with strict linear processes and a high emphasis on planning and documentation; user desires and preferences evolve continually, driving applications to adapt by putting users at the center of the design (user-centered-design) and relying on customer feedback and collaboration.
The agile development process offers a solution to the increasing uncertainty and unpredictability within the industry by promoting the faster delivery of well-designed products through self-organizing teams.
Why Choose Agile Development?
- Thrives in unpredictable and uncertain environments
- Embraces change throughout the development cycle
- Iterative processes enable rapid adaptation
- Prioritizes people and collaboration over comprehensive documentation
- Delivers value continuously, reducing waste
- Leverages self-organizing teams for greater ownership
- Prioritizes and refines requirements each iteration
- Uses frequent releases and feedback loops for ongoing improvement
Principles and Values of Agile Development
Communication & Collaboration
Teams work together—sharing creativity and perspectives—to achieve superior outcomes. By fostering an agile mindset, they select the right tools and processes for each challenge.
Project Delivery Focus
We prioritize working software over comprehensive documentation and excessive bureaucracy and long approval chains, streamlining processes to deliver value faster.
Customer & User Feedback
We gather feedback early and often, adapting requirements continuously from UX research through launch to ensure high customer satisfaction.
Agile Leadership
Strong agile leadership ensures that vision, values, and team autonomy stay aligned. Effective agile leaders empower teams to self-organize, remove impediments, and continuously refine both product and process.
Agile Development Process
Agile development is the preferred approach for mobile app projects, given the significant complexity and uncertainty involved. Our teams specialize in Agile frameworks and tools, adapting each to your needs to mitigate risks and volatility.
After the product owner defines the problems and desired outcomes, our development teams determine the optimal implementation strategy. A Scrum Master facilitates rapid, iterative delivery by guiding the team through each sprint.
Throughout each sprint, our UX researchers, as part of the integrated development team, analyze user needs, select appropriate research methods, and validate designs through artifacts and usability testing. Krasamo employs lean-Agile feedback loops to continuously refine the application based on user insights.
Key Activities Within Each Agile Sprint
In every sprint, our cross-functional teams work concurrently across several key disciplines to deliver a valuable product increment:
- Discovery and Design (UX/UI): Continuously refining requirements, conducting user research, and validating designs through prototypes and usability testing.
- Development: Building features with clean, high-quality code in close collaboration with UX and QA specialists.
- Quality Assurance: Integrating quality from the start through automated testing, peer reviews, and continuous verification of the product.
- Feedback and Adaptation: Concluding each sprint with reviews and retrospectives to incorporate feedback from stakeholders and continuously improve both the product and our process.
Agile Methodologies & Frameworks
At Krasamo, we design each project delivery process by blending the frameworks that best suit your organization’s context and goals. We examine product conditions and environments, assign teams with the right mix of skills, and maintain a flexible mindset and consistent execution throughout.
Scrum: A popular Agile methodology built around fixed-length sprints and daily stand-ups. We staff each team with a Product Owner, a Scrum Master, and a cross-functional group of Developers, which includes specialists in UX, engineering, and quality assurance, who meet every day to coordinate the next iteration. A prioritized backlog guides feature planning, drives rapid delivery, and ensures transparency across stakeholders.
SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework): A Lean-Agile framework designed to coordinate multiple teams working on complex products. SAFe organizes work into synchronized Agile Release Trains (ARTs) at the Program level, creating alignment from the Team level all the way up to the Portfolio. It integrates practices from Scrum, Kanban, DevOps, XP, and Design Thinking into a cohesive cadence of planning, execution, and continuous improvement across the enterprise.
Kanban: A visual workflow system that limits work-in-progress to improve flow and reduce bottlenecks. We implement digital Kanban boards to track tasks, define workflow states, and adjust WIP limits in real time—maximizing efficiency and ensuring that work moves smoothly from “To Do” to “Done.”
Lean-Agile: An approach that focuses on customer value and waste elimination through iterative delivery. We map end-to-end value streams, identify and remove non-value steps, and deliver incremental functionality frequently—ensuring that every delivery contributes directly to your business outcomes.
Extreme Programming (XP): An Agile methodology emphasizing technical excellence through short development cycles and rigorous testing. We adopt XP practices such as pair programming, test-driven development (TDD), continuous integration, and frequent refactoring to keep code quality high and customer requirements tightly aligned with each release.
The Agile Development Process in Practice
At Krasamo, we partner with your Product Owner to design workflows and systems tailored to your needs. Together, we maintain a living roadmap to track progress, drive continuous improvement, and adapt the Agile process to your goals.
We break work into short sprints—time-boxed cycles of incremental delivery that let teams inspect progress, incorporate feedback, and adjust course as new information emerges. This approach enables us to tackle complex challenges iteratively and embrace uncertainty with confidence.
Our small, transparent teams continuously deliver, inspect, and adapt early to avoid repeating mistakes. Our Scrum Master facilitates daily planning and removes impediments to keep everyone focused on sprint goals.
An Agile team must be cross-functional, self-organized, and flexible to solve adaptive problems and deliver superior outcomes.
Engage a Krasamo Agile team—whether established or newly formed—to implement Scrum and accelerate your product roadmap.
Scrum Artifacts
- Product Backlog (features, requirements, activities)
- Sprint Backlog
- Increment
Scrum Roles
- Scrum Master
- Product Owner
- Development Team
Scrum Events
- Sprints (1–4 weeks timebox; iterations)
- Sprint Planning
- Daily Scrums (15-minute standup)
- Sprint Review (backlog refinement)
- Sprint Retrospective (2–3 hours)
Scrum Team
- Open-minded (mindset)
- Adaptable (self-organizing)
- Continuous Learning
- Follow Process and Practices
- Build Trust and Transparency
- 3 to 9 members
An Agile process and technical excellence—along with innovative, quality design—are required for delivering high-value products.
Scrum Artifacts & Events
Product Backlog
The product backlog (also called the agile backlog) is the central guide for a team, containing items related to project goals, features, requirements, ideas, and deliverables. It is managed by the product owner. Among the most important items are user stories, which describe product features from the users’ perspective to maintain a user-centered design.
The team then creates user personas—imaginary archetypes with stories about how they will use the product. User stories are validated by design and development teams against acceptance criteria. Each story includes automated acceptance tests at the feature level, and unit tests verify the underlying code.
Backlog Refinement
Agile epics—groups of related user stories—are organized into sections to support backlog refinement. This means regularly estimating and prioritizing items to ensure successful sprint outcomes. Techniques vary by project but often include story points, affinity mapping, and T-shirt sizing to balance business value against complexity.
Sprint
Sprint planning brings the team together to assess capacity and decide which backlog items will form the sprint backlog. Sprints run two to four weeks (depending on sprint goals) and set the project’s pace. During the sprint, teams agree on which user stories to complete, estimate development time (capacity), define testing requirements, consider historical velocity, and address any other planning factors.
Daily Standups
Teams meet in a brief, face-to-face daily scrum to share progress, raise blockers, and coordinate next steps—creating visibility and enabling rapid obstacle removal.
Sprint Review
At the end of the sprint, the team demonstrates the completed Increment to stakeholders, discusses progress toward goals, and adapts the backlog as needed. This collaborative event (up to 4 hours for a one-month sprint) is a key opportunity to gather feedback that influences release decisions. This feedback may involve defining or validating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) strategy, which often spans multiple sprints to deliver core value and drive learning.
Sprint Retrospective
In the Sprint Retrospective—a dedicated meeting or workshop—the team reflects on what went well and what could improve. The team inspects its own collaboration and adapts processes to improve future sprints.
Measuring the Agile Development Process—Execution Predictability
Measuring team progress is vital for Agile development. At Krasamo, we use agile burndown charts (tracking remaining work over time) and the velocity-points method (based on average historical performance) for forecasting, not for comparing teams. We track backlog items against sprint goals, and once teams synchronize their cadence and we’ve calibrated their average velocity, we can reliably predict their capacity for future sprints. We then use automated testing and continuous integration feedback to refine our process iteratively.
Tools for Agile Development
- Asana: a web- and mobile-based work-management platform for organizing, tracking, and managing team tasks.
- Trello: a web-based, Kanban-style list-making application for visualizing and prioritizing work.
- Slack: a real-time messaging and collaboration hub that centralizes team communication.
- Jira: an issue-tracking and Agile project-management tool with customizable workflows.
- Rocket.Chat: an open-source, JavaScript-based communication platform designed for organizations with strict data-protection requirements.
- Redmine: a cross-platform, cross-database project-management web application built on Ruby on Rails.
- GitHub: an Internet-hosting service for Git repositories, offering source-code management, issue tracking, boards, and workflow automation. GitHub has GitHub Projects (Kanban-style boards) and strong CI/CD integration (via GitHub Actions).
- Confluence: A team workspace and documentation platform (integrates with Jira) used for creating product wikis, requirements, sprint notes, retrospectives, and knowledge-sharing across teams.
- Azure DevOps: Microsoft’s end-to-end DevOps platform that supports Agile planning (Scrum, Kanban), source control, CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, and reporting.
- Miro: An online collaborative whiteboard designed for distributed teams, commonly used for Agile workshops, sprint planning, retrospectives, and brainstorming sessions.
- FigJam: A collaborative whiteboard tool from Figma, ideal for mapping user journeys, storyboarding, and co-creating Agile ceremonies in real time.
Scaling Agile and DevOps
At Krasamo, our Agile development process delivers valuable software by designing innovative products with the right features aligned to user-experience goals. We complement our Agile frameworks with strategic roadmap practices to align vision and release timelines with overall delivery capacity. This roadmap provides essential context for the teams during backlog refinement and sprint planning, ensuring that every sprint contributes to the larger product strategy. Krasamo teams review this roadmap before each sprint planning session to ensure release plans stay on track.
Agile DevOps combines development and operations to boost velocity, reliability, and shared ownership. It shortens feedback loops and enables continuous delivery, giving you a faster path to customer value and a competitive edge. By integrating Scrum sprints with DevOps practices, we optimize the full application lifecycle—from initial build to large-scale system maintenance.
Through this convergence, Krasamo creates sustainable, user-centered mobile apps that deliver business advantages and improve company performance. Engage our Agile and DevOps expertise to accelerate your digital products.
Next Steps: Exploring Advanced Agile Practices
Building on our foundational overview of Agile for mobile apps, the following article—Exploring Advanced Agile Practices—dives deeper into the techniques that help teams excel in today’s fast-moving, high-stakes environment.
It examines the key drivers behind adopting Agile at scale (from skyrocketing app complexity to rigorous security and compliance needs), then unpacks proven methods such as Scrum of Scrums for cross-team coordination, Scrumban for hybrid workflows, advanced story mapping for user-focused prioritization, feature toggles with A/B testing for controlled experimentation, and mature CI/CD pipelines for reliable, automated delivery.
You’ll learn how these agile practices empower cross-functional teams to deliver secure, user-centric apps rapidly, continuously improve through data-driven feedback loops, and seamlessly integrate DevOps for end-to-end reliability and scalability.









I wholeheartedly agree with the emphasis on daily standups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives in Agile development! These practices indeed foster a culture of openness, adaptability, and continuous improvement – essential principles of lean software development 📈. Great read!
I completely agree that the Lean-Agile approach is an excellent way to prioritize customer value while eliminating waste. The emphasis on iterative delivery and end-to-end value streams resonates well with my experience in implementing the Scrum framework for software development projects. The blog post provides a concise overview of Agile methodologies, especially Lean-Agile and Extreme Programming (XP). Well-written!
Hey thanks for sharing this! Just wanted to add that in addition to using Agile epics to organize backlogs, many teams also use the scrum framework to structure their sprints. This involves breaking down work into smaller, manageable tasks (called “sprint backlog items”) and tracking progress throughout the sprint cycle. It’s a great way to ensure teams stay on track and deliver working software at the end of each iteration. 😊
Honestly, I found this overview of Agile methodology for mobile app dev to be a good primer, but it’s nothing new. The concept of lean software development is often overlooked in these types of articles.
Honestly, this blog post is kinda basic – been doing agile development for years and it’s not that hard to implement lean software development principles like daily standups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives in a mobile app dev team.
I’m not surprised Agile methodology is still the go-to approach for mobile app projects – it’s a tried-and-true framework that delivers results, especially when implemented correctly with iterative delivery and lean feedback loops.
I completely concur with the emphasis on concurrent key activities within each Agile Sprint! As someone familiar with Agile Methodology, I can attest to the efficacy of this iterative approach in delivering high-quality product increments. By integrating quality from the outset through automated testing and peer reviews, teams can identify and address potential issues promptly, thereby reducing technical debt and enhancing overall productivity.