Table of Content
- What is IIoT?
- Key Differences Between IIoT and Consumer IoT
- IIoT: Powering Industry 4.0
- The Strategic Importance of IIoT in Manufacturing
- IoT Systems Support Operations
- Top Factors Driving IIoT Adoption
- Top Benefits of Adopting IIoT
- Types of IIoT Software
- Krasamo’s IoT Offerings
- Krasamo’s Areas of IoT Experience
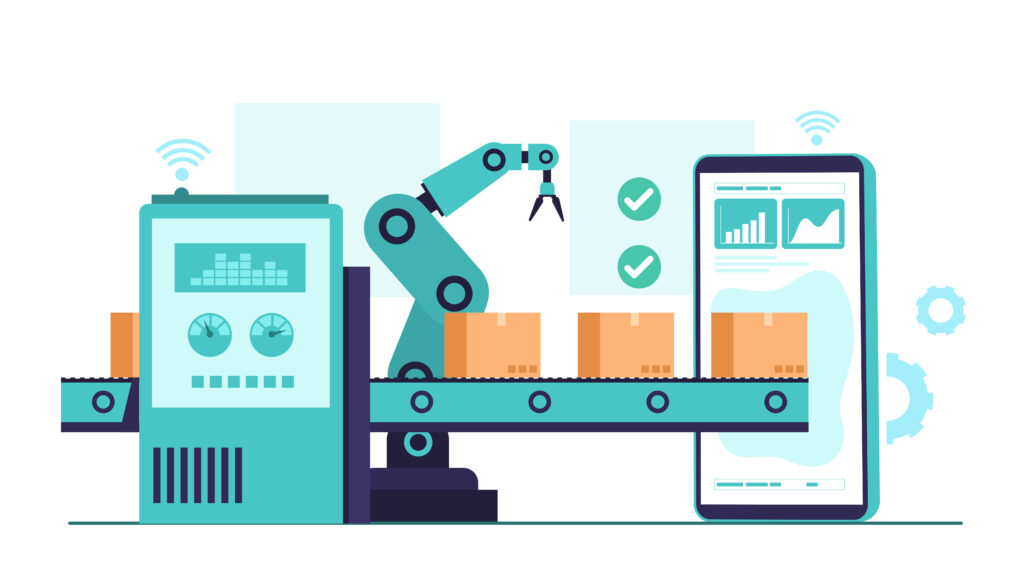
IIoT transforms industries and buildings by instrumenting physical operations with wireless sensors, data collection, advanced analytics, and machine learning.
Krasamo helps enterprises implement IIoT solutions that boost operational efficiency and reduce costs in plants and facilities. By creating IIoT systems with robust interoperability and seamless connectivity, Krasamo delivers a distinct competitive advantage.
What is IIoT?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the network of interconnected industrial devices, machines, and sensors designed specifically for use in large-scale manufacturing, supply chain management, energy, and other industrial applications.
Unlike consumer IoT, which includes devices such as smartwatches, home assistants, and connected appliances, IIoT is built to operate in complex, high-stakes industrial environments. It enables enterprise-scale automation, efficiency improvements, and real-time decision-making by integrating data from diverse sources into central business systems.
Key Differences Between IIoT and Consumer IoT
- Purpose and Scale:
While consumer IoT aims to enhance everyday living through convenience and personalized user experiences, IIoT is engineered for optimizing and automating large-scale industrial operations. IIoT applications focus on tasks such as predictive maintenance, process optimization, and real-time monitoring across factories or large facilities, driving significant improvements in operational efficiency and cost reduction - Data Volume and Complexity:
IIoT devices generate massive volumes of data that require robust data management, storage, and analysis solutions. This data is often heterogeneous and complex, demanding advanced analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) to extract actionable insights. Consumer IoT devices typically produce smaller, less complex datasets that are geared toward enhancing user interfaces and personal experiences - Integration with Enterprise Systems:
IIoT systems are integrated deeply with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, manufacturing execution systems, and other business-critical applications. This tight integration ensures that the data captured from the shop floor is immediately usable for driving strategic decisions, optimizing workflows, and even creating new revenue streams. In contrast, consumer IoT products operate largely in isolation or within personal networks, where the focus is on individual user convenience rather than enterprise-scale insights. - Security and Reliability:
Industrial environments demand high reliability and stringent security protocols. Since IIoT systems control essential functions—ranging from machinery operation to safety monitoring—the consequences of failures or breaches can be severe. Therefore, IIoT solutions are designed with advanced cybersecurity measures and real-time operational safeguards, whereas consumer IoT devices, while secure, generally do not require the same level of rigor in terms of uptime and data protection.
IIoT: Powering Industry 4.0
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is not merely about connecting devices—it is a cornerstone of digital transformation that is reshaping entire industries. As highlighted in recent strategic analyses, massive data streams generated by countless connected sensors are driving a fundamental shift in how companies operate. This transformation is fueling demand for scalable cloud infrastructures and advanced analytics that can process and extract actionable insights from complex, high-volume data sets .
Integrating IIoT with cutting-edge technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and digital twins enables organizations to achieve real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making. These capabilities lead to substantial improvements in operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower overall costs. Moreover, as industries compete in an increasingly digital marketplace, IIoT lays the groundwork for innovative business models that can open up new revenue streams and create lasting competitive advantages.
However, unlocking the full potential of IIoT requires addressing key challenges such as interoperability, cybersecurity, and the integration of legacy systems. Overcoming these difficulties is critical for ensuring robust and secure operations, and for maximizing the transformative impact of IIoT investments.
By situating IIoT within this broader digital transformation framework, enterprises can better understand its strategic importance—not just as a tool for operational improvement but as a driving force behind industry-wide innovation and market disruption.
The Strategic Importance of IIoT in Manufacturing
For stakeholders and technical teams, the key value proposition of IIoT lies in its ability to transform traditional manufacturing into a connected, agile ecosystem. By enabling seamless communication between machines, sensors, and enterprise systems, IIoT not only boosts operational efficiency but also empowers companies to implement predictive maintenance, optimize energy consumption, and enhance supply chain resilience.
Moreover, the real-time analytics enabled by IIoT allow for faster, data-driven decision making. This can lead to improved product quality, reduced downtime, and the creation of new business models that drive sustainable growth.
In today’s competitive industrial landscape, adopting IIoT is not just about staying current with technology trends—it’s about laying the foundation for a future where intelligent, interconnected systems deliver measurable business impact.
IoT Systems Support Operations
An IoT system creates a virtual model (digital twin) or a version that copies physical facilities or systems and uses its data to support operations, monitor, and perform operations, making predictions or autonomous decisions without human intervention. Smart manufacturing refers to the automated production at factories using electronics, IoT, information technology (IT), cloud computing, and data exchange to automate complex tasks for solving problems and improving operations.
IIoT leverages technologies to create a network structure and platform connected to the internet and enables the management of operations remotely.
Sensors and actuators are connected to a platform for collecting information (data) from machines and sharing it to the cloud to be stored, analyzed, and processed by machine learning models that extract insights from the physical plant process and perform analytics. IoT gateways ensure reliable connectivity by aggregating, filtering, and securely transmitting data from the field to the cloud.
Data scientists and ML engineers iterate with data to create key insights that affect the operation and share them with operators to monitor the plant and make decisions about the process’s physical aspects that may need modification or correction.
IoT edge computing plays a crucial role in this setup by processing data locally, reducing latency, and enabling real-time analytics and autonomous decision-making at the network’s edge.
IIoT creates connectivity of plant equipment (through TCP/IP) and the IoT platform that enables advanced equipment maintenance (predictive analytics) and improves asset utilization. IIoT also implements real-time streaming analytics, asset tracking, equipment monitoring, supply chain management, and others.
Top Factors Driving IIoT Adoption
Enterprises increasingly adopt IIoT to improve operational efficiency, mostly driven by cost reductions of sensors, microprocessors, storage, cloud computing, network, and bandwidth. Other factors driving the adoption of IIoT by industries are related to the improvements in hardware size and capabilities (sensors), the energy efficiency of devices with longer battery life, increased connectivity (IPV6), and available tooling, platforms, services, and software solutions.
These previously described advances enable IoT initiatives by decreasing the associated risks, lowering entry barriers and operating expenses, and increasing the profitability (ROI) of IIoT projects.
Certain restraining factors that play against the adoption of IIoT are lack of interoperability standards (communication protocols), security and privacy concerns (data leaks), lack of talent, and connectivity issues of legacy machines (not designed to connect to the internet).
Top Benefits of Adopting IIoT
Note the following benefits, consider the features and insights you need, and discuss how these apply to your IoT use case.
- Improve Asset Utilization
- Lower Operational Costs
- Improve Worker Productivity and Safety
- Improve Sustainability
- Increase Value to Users
- Create New Revenue Streams (new business models)
Types of IIoT Software
- Data Management (Big Data)
- Network Bandwidth Management
- Real-time Streaming Analytics (extracts data from sensors)
- Remote Monitoring Software
- IoT Security Solutions
Krasamo’s IoT Offerings
- Embedded Development/Firmware Development
- RTOS (operating systems)
- App Development
- IoT System Integration
- Wireless Communication Protocols
- IoT Security (network, infrastructure, data)
- Sensing Systems
- Embedded Processing Platforms
- Digital Signal Processing
- Cloud Computing
Krasamo’s Areas of IoT Experience
- Consumer Electronics
- HVAC
- Cold Chain
- Medical Devices
- Healthcare
- Semiconductors
- Document Management
- Asset Management
- Inventory Management
- Home Automation
- Commercial Building Automation
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) presents a promising opportunity for enterprises to significantly enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and foster innovation.
Krasamo, an IoT development company, offers specialized expertise and a comprehensive range of IoT services to help enterprises navigate these challenges and effectively integrate IIoT technologies into their operations. By collaborating with Krasamo, businesses can utilize the potential of IIoT and unlock new opportunities for growth and competitiveness in the rapidly evolving industrial landscape.










I completely agree that IIoT is a game-changer in industrial innovation! As an IoT consulting expert, I’ve seen firsthand the transformative power of connected ecosystems. How do you see IIoT consulting evolving in the next few years? 🤔💻